PWA Bunga! PWA Service Worker
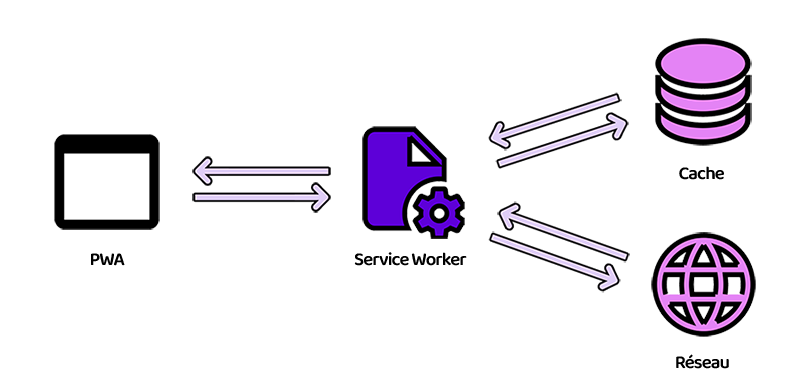
Service workers are JavaScript scripts that run in the background of your web application and enable advanced features. They act as intermediaries between the web application, the browser, and the network, allowing them to control incoming and outgoing requests and manage the caching of resources.
Service workers enable the storage of files such as images, scripts, and CSS style sheets locally on the user's device, significantly improving application performance by reducing page load times and allowing offline use of the application.
Service workers can also handle push notifications, synchronize data in the background, automatically update the application, and many other features. They provide an improved user experience and allow web applications to compete with native mobile applications.
In summary, service workers are a key component of Progressive Web Apps, offering a fast, reliable, and engaging user experience even when the user is offline or in challenging network conditions.
The serviceworker.js file of the Bunga! PWA will allow:
- serviceworker.js
Configuring cache and request processing
The serviceworker.js file of PWA Bunga! contains variables to quickly configure the cache system and request processing strategy.
Cache name and version
The cacheTitle constant is a variable that must be defined in your web application to store the name of your application. It is used for
identify cached files associated with your application. The app name should be unique and descriptive to avoid confusion with other apps.
const cacheTitle = 'yourAppName'
The cacheVersion constant is a variable that must be defined in your web application in order to store the version number of your application.
It is used to identify different sets of cached files associated with different versions of the application.
It is important to update this value each time you release a new version of your application to ensure that users
have the latest version.
const cacheVersion = 'v1.0'
The cacheName constant is a variable that combines the values of "cacheTitle" and "cacheVersion" to form a unique cache name for your application.
It is used to create a cache for your application and store files associated with this version of the application.
const cacheName = cacheTitle + '-' + cacheVersion
Cached resources
The contentToCache constant is a variable that must be defined in your web application to store a list of files to cache for use
offline. Files may include pages, images, CSS styles, JavaScript scripts, icons, and other elements necessary for the application to
works fine when offline.
const contentToCache = [
// - Pages
'/',
'index.html',
// - Favicons
'favicon.ico',
'favicon.svg',
// 'favicon-16.png',
// 'favicon-32.png',
// - CSS
'assets/css/pwabunga.css',
'assets/css/styles.css',
// - JS
'assets/js/scripts.js',
// - PWA
'pwa/css/pwabunga-ui.css',
'pwa/icons/apple-touch-icon.png',
'pwa/icons/icon-192.png',
'pwa/icons/icon-512.png',
'pwa/icons/icon-maskable-192.png',
'pwa/icons/icon-maskable-512.png',
'pwa/js/pwabunga.js',
'pwa/app.webmanifest'
]Choice of request processing strategy
The requestProcessingMethod constant is a variable that must be set in your web application to determine the strategy to use to process network requests.
It can take one of the following values: 'cacheOnly', 'networkOnly', 'cacheFirst', 'networkFirst' or 'staleWhileRevalidate'. Each value corresponds to a different strategy
to respond to network requests and to manage cached content.
cacheOnly: If this value is used, requests will be served from cache only. If the content is not available in the cache, the request will fail.cacheOnly: If this value is used, requests will be served from the network only. If the network is unreachable, the request will fail.cacheFirst: If this value is used, requests will be served from the cache first. If the content is not available in the cache, the a request will be sent to the network. If the network is not available, the request will fail.networkFirst: If this value is used, requests will be served from the network first. If the network is inaccessible, the request will be sent to the cache. If the content is not available in the cache, the request will fail.staleWhileRevalidate: If this value is used, requests will be served from cache. The contents of the cache will be returned immediately, even if it is expired. A request will be sent to the network to retrieve the latest version of the content, which will then be cached for future requests.
const requestProcessingMethod = 'cacheFirst'
Declaring a dynamic folder
The dynamicFolder constant is a variable that can be used in your web application to set the path to a dynamic folder that should not be cached.
This variable is used in conjunction with the "networkOnly" policy to ensure that requests to this folder are always served from the network and never cached.
When this variable is set, all requests that start with the defined path will be considered "networkOnly" requests. This means that these requests will always be sent to the network to be processed and that the content will never be cached.
const dynamicFolder = '/api/'
Cache handling
In order to act on the cache, we use the following functions:
Adding resources to cache
The addResourcesToCache function is an asynchronous function that can be used in your web application to add resources to the cache. This function takes a single parameter,
resources, which should be an array containing a list of all the resources you want to cache.
Explanations
Opens an instance of the application cache using the open() method of the CacheStorage API, with the cacheName variable as parameter
const cache = await caches.open(cacheName)
Uses the addAll() method to cache application resources
await cache.addAll(resources)
Full function
Note that this function is asynchronous, meaning it can be used with the await operator to wait for all resources to be added to the cache before
continue executing the code.
const addResourcesToCache = async(resources) => {
const cache = await caches.open(cacheName)
await cache.addAll(resources)
}Cache resource update
The putInCache function is an asynchronous function that can be used in your web application to cache a request and its response. This function takes two parameters,
request and response, which respectively represent the request and response you want to cache.
Explanations
Open the application cache instance
const cache = await caches.open(cacheName)
Uses the put() method to add or replace the resource in the application cache.
await cache. put(request, response)
Full function
Note that this function is asynchronous, meaning it can be used with the await operator to wait for caching to complete before
continue executing the code.
const putInCache = async(request, response) => {
const cache = await caches.open(cacheName)
await cache. put(request, response)
}Deleting a cache instance
The deleteCache function is an asynchronous function that can be used in your web application to delete a specific cache using its key.
Explanations
Use the delete() method with the key parameter, the cache entry to delete.
await caches.delete(key)
Full function
Note that this function is asynchronous, meaning it can be used with the await operator to wait for the deletion to complete before continuing
code execution.
const deleteCache = async(key) => {
await caches.delete(key)
}Removing old versions from the cache
The deleteOldCaches function is an asynchronous function that can be used in your web application to delete all caches that are not needed for
your app.
Explanations
Get the cache version instance to keep
const cacheKeepList = [cacheName]
Get the different cache instances available
const keyList = await caches.keys()
Remove from the previous variable the instance of the application cache version to keep
const cachesToDelete = keyList.filter((key) => !cacheKeepList.includes(key))
Delete old versions of the application cache using the deleteCache
await Promise.all(cachesToDelete.map(deleteCache))
Full function
Note that this function is asynchronous, meaning it can be used with the await operator to wait for the deletion to complete before continuing
code execution.
const deleteOldCaches = async() => {
const cacheKeepList = [cacheName]
const keyList = await caches.keys()
const cachesToDelete = keyList.filter((key) => !cacheKeepList.includes(key))
await Promise.all(cachesToDelete.map(deleteCache))
}Request processing strategies
Cache only
The cacheOnly function is an asynchronous function that can be used in your service worker to serve requests using cache only.
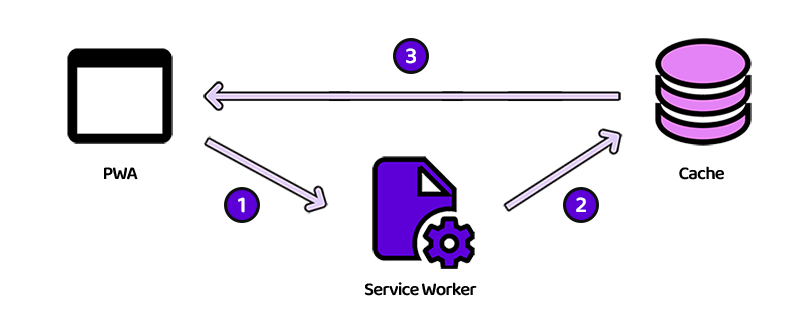
Explanations
Tests if the request has a match in the application cache with the .match() method
const responseFromCache = await caches.match(request)]
If there is a match, return the response from the cache
if (responseFromCache) {
return responseFromCache
}
Otherwise, returns a 404 response with a plain text error message
else {
return new Response("Cache error happened", {
status: 404,
headers: { "Content-Type": "text/plain" },
})
}Full function
Note that this function is asynchronous, meaning it can be used with the await operator to wait for the response before continuing code execution.
const cacheOnly = async({ request }) => {
const responseFromCache = await caches.match(request)
if (responseFromCache) {
return responseFromCache
} else {
return new Response("Cache error happened", {
status: 404,
headers: { "Content-Type": "text/plain" }
})
}
}Network only
The networkOnly function is an asynchronous function that takes an object as a parameter that contains a request to process. It first tries to retrieve the resource
requested from the network. If the network request succeeds, it returns the response. If the network request fails, it returns a 408 response with an error message.
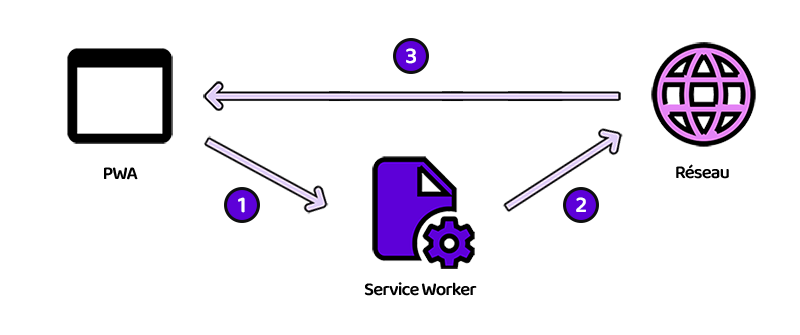
Explanations
Tests if the request finds a response on the server with the .fetch() method
const responseFromNetwork = await fetch(request)
If there is a match, return the response from the server
return responseFromNetwork
Otherwise, returns a 408 (Request Timeout) response with a "Network error happened" error message
catch (error) {
return new Response("Network error happened", {
status: 408,
headers: { "Content-Type": "text/plain" }
})
}Full function
Note that this function is asynchronous, meaning it can be used with the await operator to wait for the response before continuing code execution.
const networkOnly = async({ request }) => {
try {
const responseFromNetwork = await fetch(request)
return responseFromNetwork
} catch (error) {
return new Response("Network error happened", {
status: 408,
headers: { "Content-Type": "text/plain" }
})
}
}Cache first
The cacheFirst function is an asynchronous function that can be used in a web application to improve performance by reducing response time and the number of network requests.
This feature follows a caching strategy of first looking for the response in the cache before calling the network.
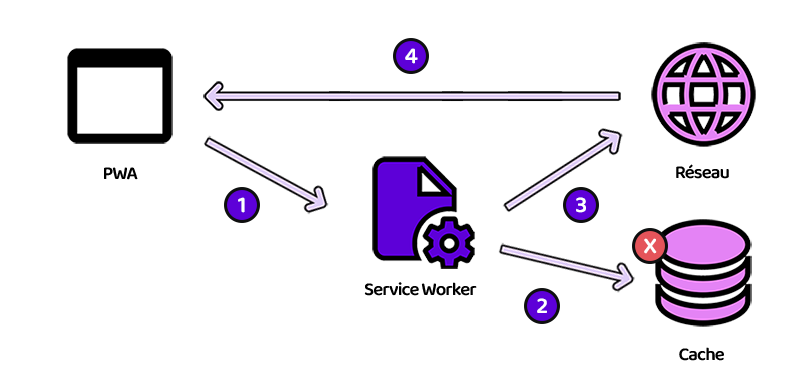
Explanations
If the request URL contains the dynamic folder (dynamicFolder)
if (request.url.includes(dynamicFolder)) {
returns response from server
return fetch(request);
Tests if the request has a match in the application cache with the .match() method
const responseFromCache = await caches.match(request)
If there is a match, return the response from the cache
if (responseFromCache) {
return responseFromCache
}
Else, test if the request has a match on the server
const responseFromNetwork = await fetch(request)if it has one, update the application cache by adding the new resource to it with the putInCache
putInCache(request, responseFromNetwork.clone())And returns the response from the server
return responseFromNetworkOtherwise, returns a 408 (Request Timeout) response with a "Network error happened" error message
catch (error) {
return new Response("Network error happened", {
status: 408,
headers: { "Content-Type": "text/plain" }
})
}Full function
Note that this function is asynchronous, meaning it can be used with the await operator to wait for the response before continuing code execution.
const cacheFirst = async ({ request }) => {
if (request.url.includes(dynamicFolder)) {
return fetch(request);
}
const responseFromCache = await caches.match(request)
if (responseFromCache) {
return responseFromCache
}
try {
const responseFromNetwork = await fetch(request)
putInCache(request, responseFromNetwork.clone())
return responseFromNetwork;
} catch (error) {
return new Response("Network error happened", {
status: 408,
headers: { "Content-Type": "text/plain" },
})
}
}Network first
The networkFirst function is an asynchronous function that can be used in your web application to retrieve a resource from the network.
If fetching from the network fails, it attempts to fetch the response from the cache.
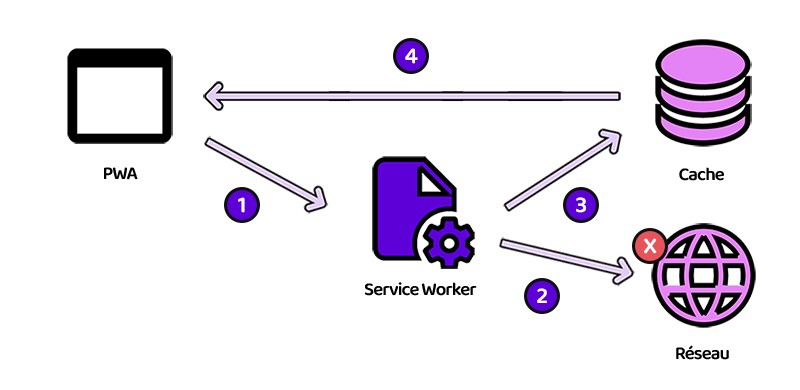
Explanations
Tests if the request has a match on the server
const responseFromNetwork = await fetch(request)if it has one, update the application cache by adding or replacing the resource with the putInCache
putInCache(request, responseFromNetwork.clone())And returns the response from the server
return responseFromNetworkOtherwise, test if the request has a match in the application cache with the .match() method
const responseFromCache = await caches.match(request)
If there is a match, return the response from the cache
if (responseFromCache) {
return responseFromCache
}
Otherwise, returns a 408 (Request Timeout) response with a "Network error happened" error message
catch (error) {
return new Response("Network error happened", {
status: 408,
headers: { "Content-Type": "text/plain" }
})
}Full function
Note that this function is asynchronous, meaning it can be used with the await operator to wait for the response before continuing code execution.
const networkFirst = async ({ request }) => {
try {
const responseFromNetwork = await fetch(request)
putInCache(request, responseFromNetwork.clone())
return responseFromNetwork;
} catch (error) {
const responseFromCache = await caches.match(request)
if (responseFromCache) {
return responseFromCache
}
return new Response("Network error happened", {
status: 408,
headers: { "Content-Type": "text/plain" }
})
}
}Stale While Revalidate
The staleWhileRevalidate function is an asynchronous function that can be used to improve the performance of web applications by
providing a quick response to a user while updating the cache version in the background.
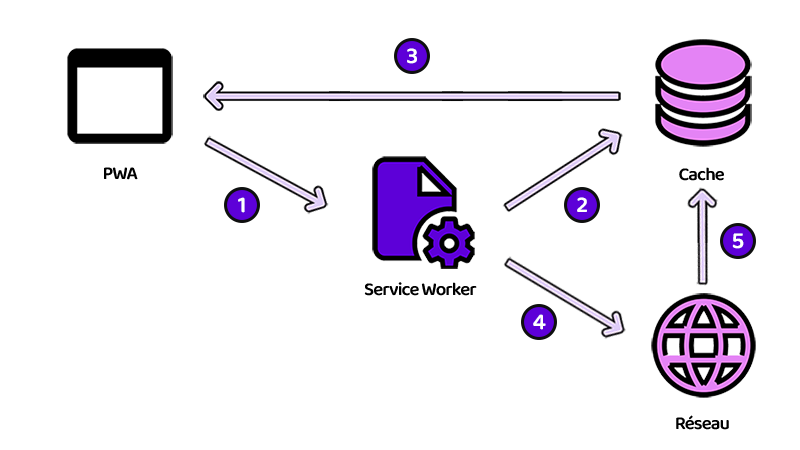
Explanations
Open the cache instance of the application using the open() method of the CacheStorage API
const cache = await caches.open(cacheName)
Tests if the request has a match in the application cache with the .match() method
const responseFromCache = await caches.match(request)]
Tests if the request finds a response on the server with the .fetch() method
const responseFromNetwork = fetch(request)
If the request has a match in the cache
if (responseFromCache) {
Creates a copy of the found response in the cache so that the original response is not modified
const responseClone = responseFromCache.clone()
Get network response
responseFromNetwork. then(response => {
Add the response retrieved from the network to the cache
cache.put(request, response.clone())
returns copy of cache response to complete function execution
return responseClone
Tries to perform a network request using the Web API fetch() method
try {
const response = await responseFromNetwork
Add the response retrieved from the network to the cache
cache.put(request, response.clone())
rSends the response retrieved from the network to complete the execution of the function.
return response
Otherwise, returns a 408 (Request Timeout) response with a "Network error happened" error message
return new Response("Network error happened", {
status: 408,
headers: { "Content-Type": "text/plain" }
})
Full function
Note that this function is asynchronous, meaning it can be used with the await operator to wait for the response before continuing code execution.
const staleWhileRevalidate = async ({ request }) => {
const cache = await caches.open(cacheName)
const responseFromCache = await caches.match(request)
const responseFromNetwork = fetch(request)
if (responseFromCache) {
const responseClone = responseFromCache.clone()
responseFromNetwork.then(response => {
cache.put(request, response.clone())
})
return responseClone
}
try {
const response = await responseFromNetwork
cache.put(request, response.clone())
return response
} catch (error) {
return new Response('Network error occurred.', {
status: 408,
headers: { 'Content-Type': 'text/plain' }
})
}
}Service worker events
Event install
This event corresponds to the installation phase of the service worker.
self.addEventListener('install', (event) => {
console.log(cacheName + 'Installation')
})Static resource caching
It is at the time of the install event that we will create the instance of the application cache with the static resources with the addResourcesToCache function.
The function uses the waitUntil method of the event object to wait for all resources to be added to the cache.
event.waitUntil(
addResourcesToCache(contentToCache)
)
Full event
self.addEventListener('install', (event) => {
console.log(cacheName + 'Installation')
event.waitUntil(
addResourcesToCache(contentToCache)
)
})
Activate event
The activate event is emitted when the service worker is downloaded and executed by the browser, and it is activated.
self.addEventListener('activate', (event) => {
})Removing application cache instances from older versions
It is during this event that we will ask the service worker to execute the function deleteOldCaches(),
in order to remove the instance from the cache of the old version of the service worker when activating the new version
event.waitUntil(
deleteOldCaches()
)
Full event
self.addEventListener('activate', (event) => {
event.waitUntil(
deleteOldCaches()
)
})
Message event
The message event will be used here to receive messages via the Message API, which allows scripts in different contexts (like a service worker and a browser window) to communicate with each other by sending messages.
self.addEventListener('message', (event) => {
})Running service worker update
When the Service worker receives the message indicating that the user has requested to perform the update (see the pwaUpdate() function of the pwabunga.js file)
if (event.data === 'SKIP_WAITING') {
The Service worker performs the update by activating the new service worker
self.skipWaiting()
Send PWA version
When the Service worker receives the message indicating that we want to display the version of the PWA (see the pwaParams() function of the pwabunga.js file)
if (event.data === 'GET_VERSION') {
For all customers associated with the service worker
self.clients.matchAll().then(function(clients) {
clients.forEach(function(client) {
Send the message containing the PWA version variable
client.postMessage(cacheVersion)
Full event
self.addEventListener('message', (event) => {
if (event.data === 'SKIP_WAITING') {
self.skipWaiting()
}
if (event.data === 'GET_VERSION') {
self.clients.matchAll().then(function(clients) {
clients.forEach(function(client) {
client.postMessage(cacheVersion)
})
})
}
})
Fetch event
The fetch event is used to manage HTTP requests from the client application.
It is used to retrieve resources from the network or the cache, depending on the configuration of the application
self.addEventListener('fetch', (event) => {
})Recovering the request
Get the request object from the fetch
const request = event.request
Request management
Defines a methods object containing possible request processing methods
const methods = {
'cacheOnly': cacheOnly,
'networkOnly': networkOnly,
'cacheFirst': cacheFirst,
'networkFirst': networkFirst,
'staleWhileRevalidate': staleWhileRevalidate
}
Retrieves the request processing method corresponding to the request method chosen in the constant requestProcessingMethod
const method = methods[requestProcessingMethod]
If a request handler method exists for the current method, it uses it to handle the request
if (method) {
event.respondWith(method({request}))
}
Full event
self.addEventListener('fetch', (event) => {
const request = event.request
const methods = {
'cacheOnly': cacheOnly,
'networkOnly': networkOnly,
'cacheFirst': cacheFirst,
'networkFirst': networkFirst,
'staleWhileRevalidate': staleWhileRevalidate
}
const method = methods[requestProcessingMethod]
if (method) {
event.respondWith(method({request}))
}
})
